G2C::Genetics
CRIPT knock-out mouse
S.G.N. Grant and the G2C Consortium
Corresponding email: Seth.Grant@ed.ac.uk
G2CMine Data Warehouse
| Cript @ G2CMine |
Genetic and Genomic Information
| Gene symbol | Cript |
| MGI ID | MGI:1929655 |
| G2Cdb mouse | G00000136 |
| Ensembl mouse | ENSMUSG00000024146 |
| G2Cdb human | G00001385 |
| Ensembl human | ENSG00000119878 |
G2CMine Data Warehouse
G2CMine integrates the scientific findings of the Genes to Cognition Programme that utilised neuroproteomics, psychiatric genetics, high-throughput mouse gene targeting combined with behavioural and electrophysiological phenotyping and informatics in order to develop a general strategy for understanding cognition at the molecular, cellular and systems neuroscience levels.
G2CMine provides comprehensive Gene Ontology, Mammalian Phenotype Ontology, Human Phenotype Ontology, UniProt, genetic and protein interactions, and regional mouse brain expression results, together with the phenotyping results of the G2C Programme.
Mutation
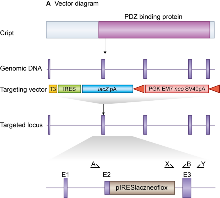
E14TG2a mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells were targeted with a vector containing 6kb and 2.5kb of flanking genomic DNA. This replaced 2kb of Cript genomic DNA (X87427053 to X87429095; Ensemble Build 55) with an IRES-lacZ-neo cassette. Genomic DNA was isolated from ES cells by Wizard SV 96 Genomic DNA purification system (Promega Cat A2371). Correctly targeted ES cells were identified by long range PCR using Expand Long Template PCR system (Roche Cat 11681842001). The PCR contained primer X (5’-GAGCTATTCCAGAAGTAGTGAG-3’) and primer Y (5’- CCAAACTGAACTCAGATCCTC -3’) that correspond to sequence in the IRES-lacZ-neo cassette and sequence outside the 2.5kb flanking region respectively. The correctly targeted ES cells were injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts to create chimeric mice, which were bred with 129S5 mice to generate heterozygous (+/–) CRIPT mutant mice. Those F1 heterozygous mice had been backcrossed with 129S5 mice for 1-2 times before being used for intercrossing.
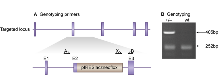
Generation of CRIPT targeted mice. Cript is 5 exon gene which encodes a protein that contains a PDZ protein binding domain (top). We replaced most of Cript exon 2 with a selection cassette in targeted mice and created a frameshift between exons 2 and 3. Primers used for genotyping(a,b & x) and targeted clone identification (x&y) are shown.
Genotyping
Genotyping PCR consisted of a 252bp product amplified from the wild-type (wt) allele using a forward primer A (GAACTACTGGGACAATTGATG) in the wt sequence deleted by targeted mutation and a reverse primer B (CTCACAGTGTCAAGCTTCAG) downstream of the cassette. A 405bp product was amplified from the targeted allele using primer B with forward primer X, within the selection cassette. After enzymatic amplification for 35 cycles (45 seconds at 94 °C, 45 seconds at 55 °C, and 1 minute at 72 °C), the PCR products were size-fractionated on a 2% agarose gel in 1x Tris borate-EDTA buffer.
Expression
Protein expression levels, evaluated by western blot, showed no reduction in protein (data not shown).
Breeding
No CRIPT-/- mice were produced from CRIPT+/- intercrosses. Male and female CRIPT+/- mice developed normally to adulthood, were fertile, exhibited normal body size and no gross abnormalities. Genotypes of 3-week-old pups from CRIPT+/- intercrosses identified 36 wt, and 95 CRIPT+/- progeny (Χ2 p= <0.001). Backcrosses onto the 129S5/SvEvBrd background were used to maintain the colony and to generate heterozygous and wildtype mice to study.
Overview
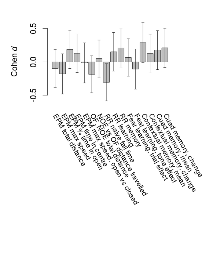
Mutant mice showed no discernible overall behavioural difference from wildtypes. With heterozygous genotype and no behavioural variables significantly affected in mutants, this mutation was deemed haplosufficient.
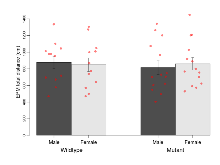
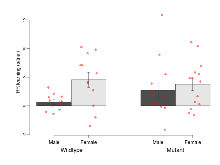
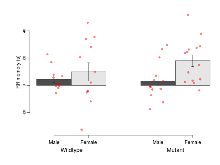
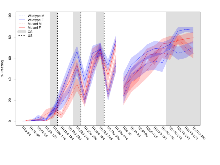
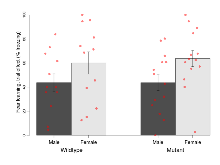
The G2CMine data warehouse provides cohort summaries and individual mouse observations from the CRIPT knock-out line phenotyping.Variables shown are: EPM total distance, Total distance (cm) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, Maximum speed (cm/s) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM % time in open, Percentage of time in the open or closed arms of the EPM spent in open arms. EPM time in centre, Total time (s) spent in the central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, open vs closed, Difference between the maximum speed (cm/s) observed in the open arms and the closed arms of the EPM. OF, NOE total distance, Total distance travelled (log₁₀ cm) during initial exposure to the open field and in presence of the novel object. NOE vs OF distance travelled, Difference in distance travelled (cm) in presence of the novel object and during initial exposure to open field. RR naive fall time, Fall time on accelerating rotarod (log₁₀ s), naive performance in session 1. RR learning, Learning on rotarod, measured as increase in fall time per trial (s/trial) in session 1. RR memory, Memory on rotarod, measured as excess fall time at middle of session 2 relative to middle of session 1. Fear learning, trial effect, Fear learning, measured as extra % time freezing before third trial compared to % time freezing before first trial. Fear learning, tone effect, Fear learning, measured as increase in % time freezing due to third tone compared to increase in % time freezing due to first tone. Contextual memory, mean, Contextual memory, measured as difference in % time freezing during first 120 s re-exposure to the box compared to first 120 s in the box on previous day. Contextual memory, change, Contextual memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the box. Cued memory, mean, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing during 120 s of tone re-exposure compared to increase in % time spent freezing during initial tone on previous day. Cued memory, change, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the tone.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=12) | Wildtype F (n=12) | Mutant M (n=14) | Mutant F (n=14) | P(sex×mutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
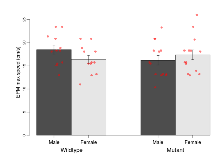
| EPM total distance | cm | 878 (72) | 850 (82) | 815 (81) | 860 (74) | 0.64 | 0.73 |
| EPM max speed | cm/s | 18.5 (1) | 16.4 (0.9) | 16.2 (1) | 17.4 (1) | 0.1 | 0.53 |
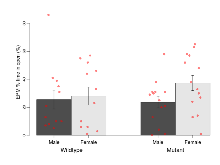
| EPM % time in open | % | 25.5 (6.7) | 28 (6.4) | 23.7 (4.2) | 37.4 (5.4) | 0.33 | 0.51 |
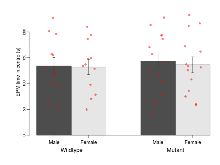
| EPM time in centre | s | 134 (16) | 132 (15) | 144 (15) | 136 (15) | 0.88 | 0.66 |
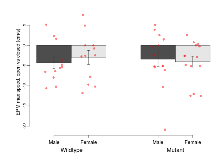
| EPM max speed, open vs closed | cm/s | -4.3 (1.4) | -3 (1.7) | -3.4 (1.8) | -4.1 (1.4) | 0.53 | 0.96 |
| OF, NOE total distance | log10 cm | 3.24 (0.09) | 3.31 (0.06) | 3.18 (0.08) | 3.26 (0.09) | 0.92 | 0.52 |
| NOE vs OF distance travelled | cm | -606 (184) | 195 (214) | -361 (100) | 14 (165) | 0.21 | 0.85 |
| RR naive fall time | log10 s | 0.94 (0.1) | 1.33 (0.09) | 0.89 (0.1) | 1.15 (0.08) | 0.49 | 0.24 |
| RR learning | s/trial | 0.7 (0.4) | 4.6 (1.3) | 2.7 (1.3) | 3.8 (1.1) | 0.22 | 0.58 |
| RR memory | s | 4.5 (2.4) | 9.9 (6.7) | 3.2 (3.7) | 18.1 (4.3) | 0.3 | 0.45 |
| Fear learning, trial effect | % freezing | 43.8 (7.2) | 60 (9.2) | 43.7 (6.6) | 63.7 (6.7) | 0.8 | 0.81 |
| Fear learning, tone effect | % freezing | 10.2 (4.3) | 10.4 (3.7) | 13.1 (5) | 4.1 (4.2) | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| Contextual memory, mean | % freezing | 35.8 (7) | 46 (7.5) | 41.6 (6) | 53.9 (6) | 0.87 | 0.31 |
| Contextual memory, change | % freezing | 16.7 (10.1) | 32.1 (6.8) | 28.6 (5.7) | 26.7 (6.8) | 0.25 | 0.66 |
| Cued memory, mean | % freezing | -0.5 (5.2) | 7.8 (3.3) | 3.5 (7.9) | 11.1 (5.6) | 0.96 | 0.54 |
| Cued memory, change | % freezing | -7.6 (6.2) | -4.7 (5.9) | -8 (5.5) | 4 (4.5) | 0.42 | 0.46 |
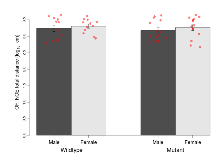
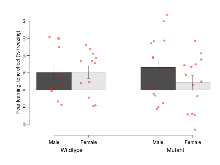
Elevated Plus Maze
Variables shown are: EPM total distance, Total distance (cm) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, Maximum speed (cm/s) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM % time in open, Percentage of time in the open or closed arms of the EPM spent in open arms. EPM time in centre, Total time (s) spent in the central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, open vs closed, Difference between the maximum speed (cm/s) observed in the open arms and the closed arms of the EPM.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=12) | Wildtype F (n=12) | Mutant M (n=14) | Mutant F (n=14) | P(sex×mutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM total distance | cm | 878 (72) | 850 (82) | 815 (81) | 860 (74) | 0.64 | 0.73 |
| EPM max speed | cm/s | 18.5 (1) | 16.4 (0.9) | 16.2 (1) | 17.4 (1) | 0.1 | 0.53 |
| EPM % time in open | % | 25.5 (6.7) | 28 (6.4) | 23.7 (4.2) | 37.4 (5.4) | 0.33 | 0.51 |
| EPM time in centre | s | 134 (16) | 132 (15) | 144 (15) | 136 (15) | 0.88 | 0.66 |
| EPM max speed, open vs closed | cm/s | -4.3 (1.4) | -3 (1.7) | -3.4 (1.8) | -4.1 (1.4) | 0.53 | 0.96 |
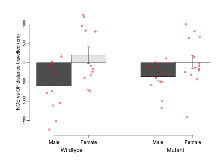
Open Field/Novel Object
Variables shown are: OF, NOE total distance, Total distance travelled (log₁₀ cm) during initial exposure to the open field and in presence of the novel object. NOE vs OF distance travelled, Difference in distance travelled (cm) in presence of the novel object and during initial exposure to open field.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=12) | Wildtype F (n=12) | Mutant M (n=14) | Mutant F (n=14) | P(sex×mutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF, NOE total distance | log10 cm | 3.24 (0.09) | 3.31 (0.06) | 3.18 (0.08) | 3.26 (0.09) | 0.92 | 0.52 |
| NOE vs OF distance travelled | cm | -606 (184) | 195 (214) | -361 (100) | 14 (165) | 0.21 | 0.85 |
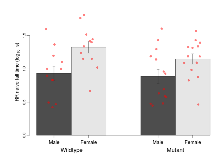
Rotarod
Variables shown are: RR naive fall time, Fall time on accelerating rotarod (log₁₀ s), naive performance in session 1. RR learning, Learning on rotarod, measured as increase in fall time per trial (s/trial) in session 1. RR memory, Memory on rotarod, measured as excess fall time at middle of session 2 relative to middle of session 1.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=12) | Wildtype F (n=12) | Mutant M (n=14) | Mutant F (n=14) | P(sex×mutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR naive fall time | log10 s | 0.94 (0.1) | 1.33 (0.09) | 0.89 (0.1) | 1.15 (0.08) | 0.49 | 0.24 |
| RR learning | s/trial | 0.7 (0.4) | 4.6 (1.3) | 2.7 (1.3) | 3.8 (1.1) | 0.22 | 0.58 |
| RR memory | s | 4.5 (2.4) | 9.9 (6.7) | 3.2 (3.7) | 18.1 (4.3) | 0.3 | 0.45 |
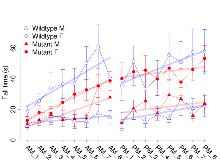
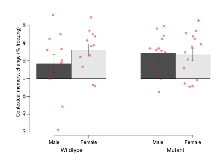
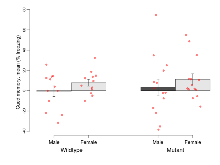
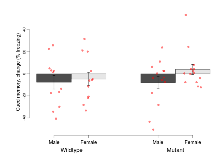
Fear Conditioning
Variables shown are: Fear learning, trial effect, Fear learning, measured as extra % time freezing before third trial compared to % time freezing before first trial. Fear learning, tone effect, Fear learning, measured as increase in % time freezing due to third tone compared to increase in % time freezing due to first tone. Contextual memory, mean, Contextual memory, measured as difference in % time freezing during first 120 s re-exposure to the box compared to first 120 s in the box on previous day. Contextual memory, change, Contextual memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the box. Cued memory, mean, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing during 120 s of tone re-exposure compared to increase in % time spent freezing during initial tone on previous day. Cued memory, change, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the tone.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=12) | Wildtype F (n=12) | Mutant M (n=14) | Mutant F (n=14) | P(sex×mutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fear learning, trial effect | % freezing | 43.8 (7.2) | 60 (9.2) | 43.7 (6.6) | 63.7 (6.7) | 0.8 | 0.81 |
| Fear learning, tone effect | % freezing | 10.2 (4.3) | 10.4 (3.7) | 13.1 (5) | 4.1 (4.2) | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| Contextual memory, mean | % freezing | 35.8 (7) | 46 (7.5) | 41.6 (6) | 53.9 (6) | 0.87 | 0.31 |
| Contextual memory, change | % freezing | 16.7 (10.1) | 32.1 (6.8) | 28.6 (5.7) | 26.7 (6.8) | 0.25 | 0.66 |
| Cued memory, mean | % freezing | -0.5 (5.2) | 7.8 (3.3) | 3.5 (7.9) | 11.1 (5.6) | 0.96 | 0.54 |
| Cued memory, change | % freezing | -7.6 (6.2) | -4.7 (5.9) | -8 (5.5) | 4 (4.5) | 0.42 | 0.46 |
Behaviour raw data
| Animals | View |
| Elevated Plus Maze | View |
| Open Field | View |
| Novel Object Exploration | View |
| Rotarod | View |