G2C::Genetics
14-3-3 θ knock-out mouse
S.G.N. Grant and the G2C Consortium
Corresponding email: Seth.Grant@ed.ac.uk
G2CMine Data Warehouse
| Ywhaq @ G2CMine |
Genetic and Genomic Information
| Gene symbol | Ywhaq |
| MGI ID | MGI:891963 |
| G2Cdb mouse | G00001058 |
| Ensembl mouse | ENSMUSG00000076432 |
| G2Cdb human | G00002307 |
| Ensembl human | ENSG00000134308 |
G2CMine Data Warehouse
G2CMine integrates the scientific findings of the Genes to Cognition Programme that utilised neuroproteomics, psychiatric genetics, high-throughput mouse gene targeting combined with behavioural and electrophysiological phenotyping and informatics in order to develop a general strategy for understanding cognition at the molecular, cellular and systems neuroscience levels.
G2CMine provides comprehensive Gene Ontology, Mammalian Phenotype Ontology, Human Phenotype Ontology, UniProt, genetic and protein interactions, and regional mouse brain expression results, together with the phenotyping results of the G2C Programme.
Mutation
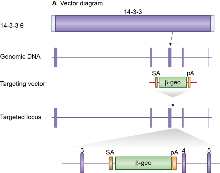
A mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell line (AL0734, strain 129/Ola) with an insertional mutation in Ywhaq was obtained from Sanger Institute Gene Trap Resource (SIGTR - sanger.ac.uk/PostGenomics/genetrap/). The insertional mutation in AL0734 by the gene-trapping vector, pGT0lxr, that was designed to create an in-frame fusion between the 5' exons of the trapped gene and a reporter, β-geo (a fusion of β-galactosidase and neomycin phosphotransferase II) occurred in intron 3-4. Thus, the gene-trapped locus is predicted to yield a fusion transcript containing exons 1-3 of Ywhaq and β-geo.
The ES cells were injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts to create chimeric mice, which were bred with 129S5 mice to generate heterozygous (+/â) Ywhaq mutant mice. Those F1 heterozygous mice had been backcrossed with 129S5 mice for 1-2 times before being used for intercrossing to produce homozygous mutants.
Location of Ywhaq gene trap. Ywhaq is a 5 exon gene which encodes a protein with a 14-3-3 domain (top). The Ywhaq gene trap is located in intron 3-4.
Genotyping
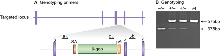
Genomic DNA was isolated from ES cells or mouse tissues by Wizard SV 96 Genomic DNA purification system (Promega Cat A2371). Genotyping PCR consisted of a 575bp product amplified from the wild-type (wt) allele using a forward primer A (5'- CAATGCAACTAATCCAGAGAG -3') upstream of the cassette and a reverse primer B (5'- CAGATTACTACCCTACATGTG -3') in the wt sequence deleted by targeted mutation. A 375bp product was amplified from the targeted allele using primer B with forward primer C (5â- GATCTGCACTGTCCCGGATG -3â), within the β-geo cassette. After enzymatic amplification for 35 cycles (45 seconds at 94 °C, 45 seconds at 55 °C, and 1 minute at 72 °C), the PCR products were size-fractionated on a 2% agarose gel in 1x Tris borate-EDTA buffer.
Primers used for genotyping (a,b & c). PCR genotyping of gene trap 14-3-3 θ mice using a common reverse primer, b, and forward primers a and c to amplify the wt and mutant alleles respectively.
Expression
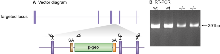
Total RNA (100µg) was isolated from ES cells with RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Cat 74104). RT-PCR was performed by generating first strand cDNA using Oligo(dT)12-18 primer (Invitrogen, Cat 18418-012) and superscript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen, Cat 18064-071). RT-PCR consisted of a 391bp product amplified from the wild-type (wt) cDNA using a forward primer Y (5â- CTTGATACACTGAACGAAGAC -3â) upstream of the cassette and a reverse primer Z (5â- GTGTCTGGAAGTTACTCGTG -3â) downstream of the insertion site. To confirm the location of the gene trap RT-PCR consisted of a 310bp product was amplified from the gene trap cDNA using primer W (5â- GACACCTCTGACAAGAAGTTG -3â) upstream of the cassette with reverse primer X (5â- GATCCTCTAGAGTCCAGATCTG -3â), within the β-geo cassette. After enzymatic amplification for 35 cycles (45 seconds at 94 °C, 1 minute at 55 °C, and 1 minute at 72 °C), the PCR products were size-fractionated on a 2% agarose gel in 1x Tris borate-EDTA buffer.
Primers used for RT-PCR (w,x,y & z) RT-PCR to detect loss of RNA - forward primer y (in exon 4) and reverse primer z (in exon 5) show amplification is weaker in homozygous mice where the gene trap cassette has been inserted. RT-PCR - forward primer w (in exon 3) and reverse primer x (within the gene trap cassette) were used to confirm the location of the trap (image not shown).
Breeding
Birth of 14-3-3 θ-/- mice followed Mendelian ratios with 19% of offspring being homozygous knockouts. Genotypes of 3-week-old pups from 14-3-3 θ+/- intercrosses identified 33 wt, 51 14-3-3 θ+/- and 19 14-3-3 θ-/- progeny (Χ2 p= 0.148). Male and female 14-3-3 θ-/- mice developed normally to adulthood, exhibited normal body size and no gross abnormalities. 14-3-3 θ mice were maintained by backcrossing onto the 129S5/SvEvBrd background; heterozygous males and females were fertile and used to set up intercrosses to generate homozygous and wildtype mice to study.
Overview
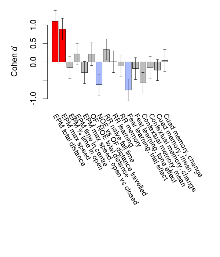
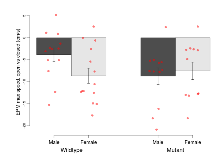
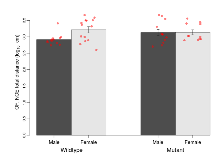
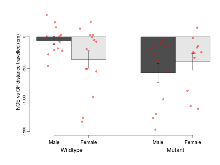
Mutant mice showed little overall behavioural difference from wildtypes, with four of 16 behaviour variables significantly impacted in these mutants. In the elevated plus maze task, two behavioural variables of five were significantly impacted in mutants. In the open field/novel object exploration task, one behavioural variable, NOE vs OF distance travelled, was significantly decreased in mutants. In the fear learning task, one behavioural variable, fear learning trial effect, was significantly decreased in mutants. Rotarod, contextual memory and cued memory tasks were unaffected. Definitions of variables may be found below.
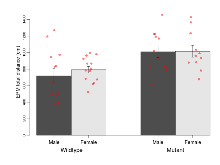
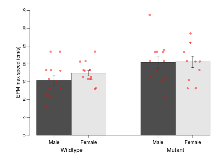
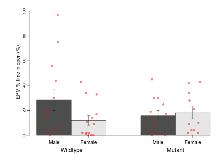
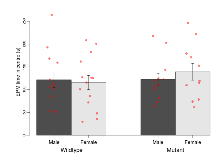
The G2CMine data warehouse provides cohort summaries and individual mouse observations from the 14-3-3 θ knock-out line phenotyping.Variables shown are: EPM total distance, Total distance (cm) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, Maximum speed (cm/s) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM % time in open, Percentage of time in the open or closed arms of the EPM spent in open arms. EPM time in centre, Total time (s) spent in the central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, open vs closed, Difference between the maximum speed (cm/s) observed in the open arms and the closed arms of the EPM. OF, NOE total distance, Total distance travelled (logââ cm) during initial exposure to the open field and in presence of the novel object. NOE vs OF distance travelled, Difference in distance travelled (cm) in presence of the novel object and during initial exposure to open field. RR naive fall time, Fall time on accelerating rotarod (logââ s), naive performance in session 1. RR learning, Learning on rotarod, measured as increase in fall time per trial (s/trial) in session 1. RR memory, Memory on rotarod, measured as excess fall time at middle of session 2 relative to middle of session 1. Fear learning, trial effect, Fear learning, measured as extra % time freezing before third trial compared to % time freezing before first trial. Fear learning, tone effect, Fear learning, measured as increase in % time freezing due to third tone compared to increase in % time freezing due to first tone. Contextual memory, mean, Contextual memory, measured as difference in % time freezing during first 120 s re-exposure to the box compared to first 120 s in the box on previous day. Contextual memory, change, Contextual memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the box. Cued memory, mean, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing during 120 s of tone re-exposure compared to increase in % time spent freezing during initial tone on previous day. Cued memory, change, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the tone.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=13) | Wildtype F (n=14) | Mutant M (n=12) | Mutant F (n=11) | P(sexÃmutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM total distance | cm | 719 (86) | 792 (40) | 1010 (71) | 1016 (71) | 0.62 | 0.00047 *** |
| EPM max speed | cm/s | 15.4 (1.3) | 17.4 (0.8) | 20.5 (1.7) | 20.6 (1.6) | 0.47 | 0.0036 ** |
| EPM % time in open | % | 28.6 (8.6) | 12 (3.9) | 15.8 (4.2) | 18.1 (4.9) | 0.11 | 0.56 |
| EPM time in centre | s | 122 (17) | 116 (16) | 122 (14) | 139 (18) | 0.49 | 0.47 |
| EPM max speed, open vs closed | cm/s | -3.8 (1.5) | -8.6 (1.7) | -8.7 (1.9) | -7.5 (2) | 0.098 | 0.29 |
| OF, NOE total distance | log10 cm | 2.92 (0.05) | 3.22 (0.09) | 3.13 (0.1) | 3.14 (0.08) | 0.082 | 0.4 |
| NOE vs OF distance travelled | cm | -59 (61) | -359 (138) | -570 (151) | -395 (130) | 0.064 | 0.033 * |
| RR naive fall time | log10 s | 1.04 (0.08) | 1.21 (0.1) | 1.18 (0.12) | 1.33 (0.12) | 0.95 | 0.23 |
| RR learning | s/trial | 1.8 (0.6) | 1.6 (1.3) | 0.5 (0.4) | 3 (2) | 0.28 | 0.96 |
| RR memory | s | 12.4 (4.3) | 5.4 (5.3) | 6.7 (3.9) | 6.9 (7.1) | 0.5 | 0.69 |
| Fear learning, trial effect | % freezing | 63.9 (6.1) | 60.3 (7.3) | 41.1 (7.6) | 44.3 (9) | 0.65 | 0.013 * |
| Fear learning, tone effect | % freezing | 8.5 (6.5) | 11.8 (5.8) | 7.6 (7.6) | 4.6 (6.6) | 0.64 | 0.55 |
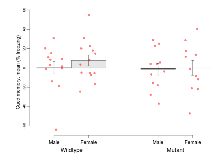
| Contextual memory, mean | % freezing | 48 (6.6) | 48.1 (5) | 43.1 (6.7) | 29.3 (4.5) | 0.24 | 0.051 |
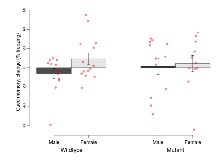
| Contextual memory, change | % freezing | 22.9 (7.5) | 34.6 (7.6) | 23.4 (8.2) | 26.6 (7) | 0.58 | 0.63 |
| Cued memory, mean | % freezing | 0.2 (6.4) | 7.8 (5.6) | -1.4 (6) | 0.1 (7.7) | 0.64 | 0.47 |
| Cued memory, change | % freezing | -6 (5.1) | 9.2 (6) | 1.4 (8.3) | 4.4 (8.4) | 0.38 | 0.85 |
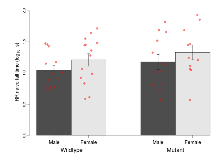
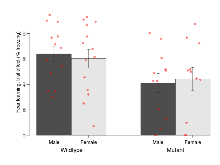
Elevated Plus Maze
Variables shown are: EPM total distance, Total distance (cm) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, Maximum speed (cm/s) travelled in any arm or central zone of the EPM. EPM % time in open, Percentage of time in the open or closed arms of the EPM spent in open arms. EPM time in centre, Total time (s) spent in the central zone of the EPM. EPM max speed, open vs closed, Difference between the maximum speed (cm/s) observed in the open arms and the closed arms of the EPM.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=13) | Wildtype F (n=14) | Mutant M (n=12) | Mutant F (n=11) | P(sexÃmutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM total distance | cm | 719 (86) | 792 (40) | 1010 (71) | 1016 (71) | 0.62 | 0.00047 *** |
| EPM max speed | cm/s | 15.4 (1.3) | 17.4 (0.8) | 20.5 (1.7) | 20.6 (1.6) | 0.47 | 0.0036 ** |
| EPM % time in open | % | 28.6 (8.6) | 12 (3.9) | 15.8 (4.2) | 18.1 (4.9) | 0.11 | 0.56 |
| EPM time in centre | s | 122 (17) | 116 (16) | 122 (14) | 139 (18) | 0.49 | 0.47 |
| EPM max speed, open vs closed | cm/s | -3.8 (1.5) | -8.6 (1.7) | -8.7 (1.9) | -7.5 (2) | 0.098 | 0.29 |
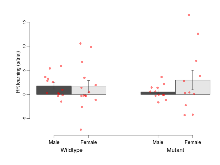
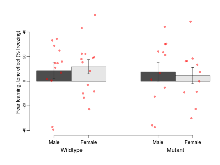
Open Field/Novel Object
Variables shown are: OF, NOE total distance, Total distance travelled (logââ cm) during initial exposure to the open field and in presence of the novel object. NOE vs OF distance travelled, Difference in distance travelled (cm) in presence of the novel object and during initial exposure to open field.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=13) | Wildtype F (n=14) | Mutant M (n=12) | Mutant F (n=11) | P(sexÃmutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF, NOE total distance | log10 cm | 2.92 (0.05) | 3.22 (0.09) | 3.13 (0.1) | 3.14 (0.08) | 0.082 | 0.4 |
| NOE vs OF distance travelled | cm | -59 (61) | -359 (138) | -570 (151) | -395 (130) | 0.064 | 0.033 * |
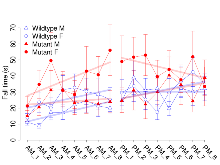
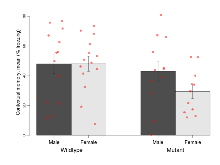
Rotarod
Variables shown are: RR naive fall time, Fall time on accelerating rotarod (logââ s), naive performance in session 1. RR learning, Learning on rotarod, measured as increase in fall time per trial (s/trial) in session 1. RR memory, Memory on rotarod, measured as excess fall time at middle of session 2 relative to middle of session 1.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=13) | Wildtype F (n=14) | Mutant M (n=12) | Mutant F (n=11) | P(sexÃmutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR naive fall time | log10 s | 1.04 (0.08) | 1.21 (0.1) | 1.18 (0.12) | 1.33 (0.12) | 0.95 | 0.23 |
| RR learning | s/trial | 1.8 (0.6) | 1.6 (1.3) | 0.5 (0.4) | 3 (2) | 0.28 | 0.96 |
| RR memory | s | 12.4 (4.3) | 5.4 (5.3) | 6.7 (3.9) | 6.9 (7.1) | 0.5 | 0.69 |
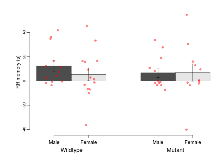
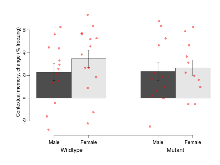
Fear Conditioning
Variables shown are: Fear learning, trial effect, Fear learning, measured as extra % time freezing before third trial compared to % time freezing before first trial. Fear learning, tone effect, Fear learning, measured as increase in % time freezing due to third tone compared to increase in % time freezing due to first tone. Contextual memory, mean, Contextual memory, measured as difference in % time freezing during first 120 s re-exposure to the box compared to first 120 s in the box on previous day. Contextual memory, change, Contextual memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the box. Cued memory, mean, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing during 120 s of tone re-exposure compared to increase in % time spent freezing during initial tone on previous day. Cued memory, change, Cued memory, measured as increase in % time spent freezing from first time bin of 30 s to fourth bin of 30 s during 120 s re-exposure to the tone.
| Variable | Units | Wildtype M (n=13) | Wildtype F (n=14) | Mutant M (n=12) | Mutant F (n=11) | P(sexÃmutation) | P(mutation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fear learning, trial effect | % freezing | 63.9 (6.1) | 60.3 (7.3) | 41.1 (7.6) | 44.3 (9) | 0.65 | 0.013 * |
| Fear learning, tone effect | % freezing | 8.5 (6.5) | 11.8 (5.8) | 7.6 (7.6) | 4.6 (6.6) | 0.64 | 0.55 |
| Contextual memory, mean | % freezing | 48 (6.6) | 48.1 (5) | 43.1 (6.7) | 29.3 (4.5) | 0.24 | 0.051 |
| Contextual memory, change | % freezing | 22.9 (7.5) | 34.6 (7.6) | 23.4 (8.2) | 26.6 (7) | 0.58 | 0.63 |
| Cued memory, mean | % freezing | 0.2 (6.4) | 7.8 (5.6) | -1.4 (6) | 0.1 (7.7) | 0.64 | 0.47 |
| Cued memory, change | % freezing | -6 (5.1) | 9.2 (6) | 1.4 (8.3) | 4.4 (8.4) | 0.38 | 0.85 |
Behaviour raw data
| Animals | View |
| Elevated Plus Maze | View |
| Open Field | View |
| Novel Object Exploration | View |
| Rotarod | View |