G2C::Genetics
TNIK is required for postsynaptic and nuclear signalling pathways and cognitive function
Marcello P. Coba1,2*, Noboru H. Komiyama1,3*, Jess Nithianantharajah1,3*, Maksym V. Kopanitsa1,4, Tim Indersmitten5, Nathan G. Skene1, Ellie J. Tuck1,4, David G. Fricker1,4, Kathryn A. Elsegood1,3, Lianne E. Stanford1, Nurudeen Afinowi1,4, Lisa M. Saksida6, Timothy J. Bussey6, Thomas J. O'Dell7 and Seth G.N. Grant1,3,6
Author email: Seth.Grant@ed.ac.uk * - These authors contributed equally to this work
- Genes to Cognition Programme, The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridgeshire, CB10 1SA, UK
- Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, 90089, USA
- Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences and Centre for Neuroregeneration, The University of Edinburgh, Chancellors Building, 47 Little France Crescent, Edinburgh EH16 4SB, UK
- Synome Ltd, Babraham Research Campus, Cambridge, CB22 3AT, UK
- Interdepartmental PhD Program for Neuroscience, UCLA, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
- Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge, UK; The MRC and Wellcome Trust Behavioural and Clinical Neuroscience Institute, University of Cambridge, Downing St., Cambridge CB2 3EB, UK
- Department of Physiology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, California 90095, USA
Traf2 and NcK interacting Kinase (TNiK) contains serine-threonine kinase and scaffold domains and has been implicated in cell proliferation and glutamate receptor regulation in vitro. Here we report its role in vivo using mice carrying a knockout mutation.
TNiK binds protein complexes in the synapse linking it to the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) via AKAP9. NMDAR and metabotropic receptors bidirectionally regulate TNiK phosphorylation and TNiK was required for AMPA expression and synaptic function. TNiK also organises nuclear complexes and in the absence of TNiK, there was a marked elevation in GSK3Β and phosphorylation levels of its cognate phosphorylation sites on NeuroD1 with alterations in Wnt pathway signalling.
We observed impairments in dentate gyrus neurogenesis in TNiK knockout mice and cognitive testing using the touchscreen apparatus revealed impairments in pattern separation on a test of spatial discrimination. Object-location paired associates learning, which is dependent on glutamatergic signalling was also impaired. Additionally, TNiK knockout mice displayed hyperlocomotor behavior that could be rapidly reversed by GSK3Β inhibitors, indicating the potential for pharmacological rescue of a behavioral phenotype.
These data establish TNiK as a critical regulator of cognitive functions and suggest it may play a regulatory role in diseases impacting on its interacting proteins and complexes.
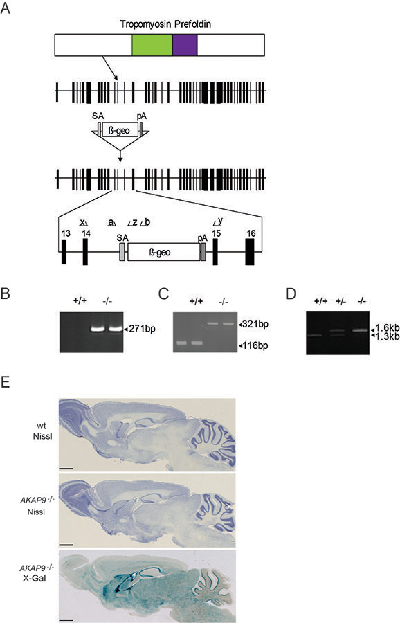
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of AKAP9 mutant mice
A mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell line (XP0050, strain 129/Ola) with an insertional mutation in Akap9 was obtained from Sanger Institute Gene Trap Resource (SIGTR - sanger.ac.uk/PostGenomics/genetrap/). The insertional mutation in XP0050 by the gene-trapping vector, pGT0lxr, was designed to create an in-frame fusion between the 5' exons of the trapped gene and a reporter, Β-geo (a fusion of Β-galactosidase and neomycin phosphotransferase II) occurred in intron 14-15 (Transcript: Akap9-001 (ENSMUST00000044492) Ensembl release 56). Thus, the gene-trapped locus is predicted to yield a fusion transcript containing exons 1-14 of Akap9 and Β-geo. Integration of the gene-trapping vector was confirmed by RT-PCR. A 217bp product was amplified from the gene trap clone cDNA using primer x (GAAGCTGTCTAAGAGAGTGTG) that hybridises the sequence encoded by the part of exon 14 with reverse Primer z (GATCCTCTAGAGTCCAGATCTG) within the Β-geo cassette. This gene trap ES cell clone was injected into C57/BL6 blastocysts to create chimeric mice, which were bred with 129S5 mice to generate heterozygous (+/–) Akap9 mutant mice. Those F1 heterozygous mice had been backcrossed with 129S5 mice for 1-2 times before being used for intercrossing.
A. Gene trap vector for the generation of AKAP9 knockout mice. Linear structure of AKAP9 protein domain (top diagram). AKAP9 is a 48 exon protein. The gene-trapping vector, pGT0lxr, is inserted between exon14 and 15. Primers used for genotyping (see supplementary methods) are shown (bottom diagram). SA, splice acceptor; pA, polyadenylation signal; Β-geo, fusion of Β-galactosidase and neomycin phosphotransferase II.
B. Electrophoresis gel image showing confirmation by RTPCR that trap is correctly inserted.
C. RT-PCR genotyping. Homozygote (-/-) product is 205bp larger than wt (+/+) product.
D. PCR genotyping of targeted AKAP9-/- mice using a common forward primer, a, and reverse primers b and y to amplify the wt and mutant alleles respectively.
Supplementary Table 1. Hippocampal mRNA expression profile of TNiK-/- mice
Shown are the 200 most significant genes from the mRNA expression profiling, the whole genome array results are downloadable.
Download whole genome microarray results
| Gene Symbol | Gene Description | Ensembl Gene ID | Entrez Gene ID | Average Expression | log Fold Change | P Value | Adjusted P Value | t | Genomic Location | Probe Location | RefSeq transcripts | Probe id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spata13 | Spermatogenesis associated 13 | ENSMUSG00000021990 | 9.20 | -0.357 | 6.44E-09 | 1.49E-04 | -7.17 | chr14:61383157:61383206:+ | 3pUTR | XM_923227 XM_901902 | ILMN_2751037 | |
| Cort | Cortistatin | ENSMUSG00000028971 | 258453 | 8.40 | 0.378 | 3.32E-08 | 3.84E-04 | 6.69 | chr4:148499369:148499418:- | CDS | NM_007745 | ILMN_1226607 |
| BC050868 | Mus musculus adult male cerebellum cDNA, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone:1500031A17 product:TRAF2 AND NCK INTERACTING KINASE, SPLICE VARIANT 8 homolog [Homo sapiens], full insert sequence. | ENSMUSG00000027692 | 10.07 | -0.403 | 6.85E-08 | 5.28E-04 | -6.47 | chr3:28569142:28569191:+ | 3pUTR | XM_001473621 XM_001473602 XM_001474909 XM_001474897 | ILMN_2524251 | |
| C4b | Complement component 4B (Childo blood group) | ENSMUSG00000073418 | 212285 | 8.68 | -0.335 | 3.40E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.32 | chr17:34866134:34866183:- | CDS | NM_009780 NM_011413 XM_973028 XM_972987 XM_973068 | ILMN_1215092 |
| Scara3 | Scavenger receptor class A, member 3 | ENSMUSG00000034463 | 268996 | 10.26 | -0.283 | 5.07E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.20 | chr14:66538293:66538342:- | 3pUTR | NM_172604 | ILMN_2706268 |
| Slc30a3 | Solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter), member 3 | ENSMUSG00000029151 | 22784 | 12.22 | -0.283 | 5.20E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.19 | chr5:31388548:31388597:- | 3pUTR | ILMN_2521965 | |
| C4b | Complement component 4B (Childo blood group) | ENSMUSG00000015451 | 78829 | 8.53 | -0.288 | 5.82E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.15 | chr17:34865420:34865469:- | CDS | NM_009780 NM_011413 XM_973028 XM_972987 XM_973068 | ILMN_3049559 |
| Tcirg1 | T-cell, immune regulator 1, ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal V0 protein A3 | ENSMUSG00000001750 | 258203 | 7.57 | -0.103 | 6.47E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.12 | chr19:3903583:3903632:- | CDS | NM_016921 | ILMN_2643879 |
| Hn1 | Hematological and neurological expressed sequence 1 | ENSMUSG00000020737 | 69202 | 12.59 | -0.196 | 6.80E-06 | 1.66E-02 | -5.11 | chr11:115358689:115358738:- | 3pUTR | NM_008258 | ILMN_2914744 |
| Cox6a2 | Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit VI a, polypeptide 2 | ENSMUSG00000030785 | 258289 | 8.53 | 0.336 | 7.19E-06 | 1.66E-02 | 5.09 | chr7:135349162:135349211:- | 3pUTR | NM_009943 | ILMN_2629581 |
| 9130213B05Rik | RIKEN cDNA 9130213B05 gene | ENSMUSG00000034981 | 231440 | 11.20 | 0.437 | 1.20E-05 | 2.23E-02 | 4.93 | chr5:92052926:92052975:+ | 3pUTR | NM_145562 | ILMN_2756704 |
| Ebf3 | Early B-cell factor 3 | ENSMUSG00000010476 | 7.95 | 0.127 | 1.22E-05 | 2.23E-02 | 4.93 | chr7:144385579:144385628:- | 3pUTR | NM_001113414 NM_001113415 NM_010096 | ILMN_2422615 | |
| Rhag | Rhesus blood group-associated A glycoprotein | ENSMUSG00000023926 | 16428 | 7.55 | -0.084 | 1.25E-05 | 2.23E-02 | -4.92 | chr17:40971620:40971669:+ | CDS | NM_011269 | ILMN_2745515 |
| Rabggtb | RAB geranylgeranyl transferase, b subunit | ENSMUSG00000038975 | 338360 | 7.74 | -0.146 | 1.64E-05 | 2.70E-02 | -4.84 | chr3:153573046:153573095:- | 3pUTR | ILMN_2703263 | |
| Myo5b | Myosin VB | ENSMUSG00000025885 | 17919 | 9.94 | -0.423 | 2.07E-05 | 3.19E-02 | -4.77 | chr18:74930039:74930088:+ | CDS | NM_201600 | ILMN_2539489 |
| A830018L16Rik | RIKEN cDNA A830018L16 gene | 69035 | 8.72 | -0.210 | 2.23E-05 | 3.23E-02 | -4.75 | chr1:11588290:11588339:+ | 3pUTR | ILMN_1213044 | ||
| Nat8l | N-acetyltransferase 8-like | ENSMUSG00000048142 | 56208 | 9.72 | 0.284 | 2.59E-05 | 3.53E-02 | 4.70 | chr5:34345517:34345566:+ | 3pUTR | NM_001001985 | ILMN_2594039 |
| Grasp | GRP1 (general receptor for phosphoinositides 1)-associated scaffold protein | ENSMUSG00000000531 | 67692 | 11.35 | -0.216 | 2.84E-05 | 3.64E-02 | -4.67 | chr15:101063106:101063155:+ | 3pUTR | NM_019518 | ILMN_2596396 |
| Usp52 | Ubiquitin specific peptidase 52 | ENSMUSG00000005682 | 74559 | 8.57 | -0.254 | 3.42E-05 | 3.66E-02 | -4.61 | chr10:127758185:127758234:+ | 3pUTR | NM_133992 | ILMN_2790392 |
| Bat2d | BAT2 domain containing 1 | ENSMUSG00000040225 | 71983 | 7.82 | 0.305 | 3.67E-05 | 3.66E-02 | 4.59 | chr1:164640509:164640558:- | CDS | NM_001081290 | ILMN_1239599 |
| Lum | Lumican | ENSMUSG00000036446 | 8.24 | -0.279 | 3.72E-05 | 3.66E-02 | -4.59 | chr10:97034583:97034632:+ | CDS | NM_008524 | ILMN_3001540 | |
| Tle1 | Transducin-like enhancer of split 1, homolog of Drosophila E(spl) | ENSMUSG00000008305 | 240667 | 8.62 | -0.275 | 4.25E-05 | 3.66E-02 | -4.55 | chr4:71819008:71819057:- | 3pUTR | ILMN_1245089 | |
| Ifnz | Interferon zeta | ENSMUSG00000073810 | 74753 | 7.59 | -0.089 | 4.58E-05 | 3.66E-02 | -4.52 | chr4:88428166:88428215:+ | 5pUTR | NM_197889 | ILMN_3021483 |
| B4galnt4 | Beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 4 | 330671 | 8.51 | -0.178 | 4.67E-05 | 3.66E-02 | -4.52 | chr7:148254691:148254740:+ | CDS | ILMN_2540866 | ||
| Zzz3 | Zinc finger, ZZ domain containing 3 | ENSMUSG00000039068 | 15481 | 7.61 | 0.093 | 4.68E-05 | 3.66E-02 | 4.52 | chr3:152085636:152085685:+ | 5pUTR | XR_001912 XR_032051 NM_198416 NM_001080755 | ILMN_2424408 |
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used in WB, IP, IHC and IF assays
List of antibodies used in biochemical assays. Antibody: antibody target; Assay: assay in which the antibody was used; Dilution/concentration: Dilution and/or concentration used for each antibody; Company and Catalogue Number: company name and catalogue number for commercially available antibodies.
| Antibody | Assay | Dilution/concentration | Company | Catalogue Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b-catenin | WB | 1/2000 | Cell signaling | 9582 |
| CRMP2 | WB-IP | 1/1000 - 1ug/100ul | Cell Signaling | 9393 |
| CRMP2 pT514 | WB | 1/1000 | Cell Signaling | 9397 |
| DISC1 | WB-IP | 1ug/ml- 1ug/100ul | Invitrogen | 40-6800 |
| DISC1 | WB-IP | 1ug/ml- 1ug/100ul | Invitrogen | 40-6900 |
| DISC1 | WB | 1/500 | Gift from Nick Brandon | n/a |
| Doublecortin | IHC | 1/250 | Cell signaling | 4604 |
| GluR1 | WB-IP | 1/5000 - 1ug/100ul | Millipore | AB1504 |
| GluR1 | WB-IP | 1/2000 - 1ug/100ul | Millipore | 05-855 |
| GlurR1 | WB | 1/1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-7609 |
| GSK3-b | WB-IP | 1/1000 | Cell Signaling | 9332 |
| Ki67 | IF | 1/300 | Abcam | ab15580 |
| NeuroD1 | WB | 1/1000 | Cell signaling | 4373 |
| NeuroD1 | IF | 1/500 | Abcam | ab60704 |
| NeuroD1 pS274 | WB | 1/1000 | Abcam | ab78900 |
| NR1 | WB-IP | 1/1000 - 1ug/100ul | Invitrogen | 32-0500 |
| NR1 | IP | 1ug/100ul | Created in house | n/a |
| NR1 | WB | 1ug/ml | Millipore | 06-311 |
| NR2B | WB | 1ug/ml | Millipore | 05-920 |
| NR2B | WB | 1/2000 - 1ug/100ul | Millipore | 06-600 |
| PSD95 | WB | 1/10000 | Thermo | MA1-045 |
| PSD95 pT19 | WB | 1ug/ml | Abcam | ab16496 |
| PSD95 pS418 | WB | 1ug/ml | Abcam | ab16493 |
| Tau pS396 | WB | 1/1000 | Gift from Michel Goedert | n/a |
| TNiK | WB-IP | 0.5ug/ml- 0.25ug/100ul | BD biosciences | 612250 |
| TNiK | WB | 1/10000 | Santa Cruz | sc-100206 |
| TNiK | WB | 1ug/ml- 0.5ug/100ul | Sigma | HPA012128 |
| TNiK | IP | 1ug/100ul | Thermo | PA1-20639 |
| TNiK pS735 | WB-IP | 1ug/ml- 1ug/100ul | Santa Cruz | sc-130221 |
| Tubulin | WB | 1ug/ml | Millipore | 05-559 |